Explaining Mandibular Nerve to kids
Welcome, young curious minds, to the world of the mandibular nerve! Today, we embark on an exciting journey to understand one of the essential components of our amazing human body – the nerve responsible for sensation in our jaws and mouth. Throughout this article, we will explore the fascinating world of the mandibular nerve, its function, and its importance in our daily lives. So, let’s get started!
Understanding the Human Nervous System
Before delving into the specifics of the mandibular nerve, it is crucial to have a basic understanding of the human nervous system. Our nervous system is like a complex network of communication channels, transmitting messages between different parts of our body and our brain. Nerves play a vital role in this system, acting as messengers carrying signals back and forth.
The nervous system can be divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all the nerves outside the CNS. These two systems work together seamlessly to regulate bodily functions, interpret sensory information, and coordinate responses to stimuli.
The Role of Nerves in Our Body
Nerves are specialized cells responsible for transmitting signals or messages, called nerve impulses, between different parts of our body and the brain. They act as highways, enabling communication and coordination. Without nerves, our body would struggle to function efficiently.
Within the PNS, there are sensory nerves that carry information from the body to the brain and motor nerves that transmit signals from the brain to the muscles, enabling movement. This intricate network of nerves allows us to perceive the world around us, react to stimuli, and carry out complex tasks with precision.
The Basic Structure of a Nerve
Now, let’s take a closer look at the structure of a nerve. Nerves consist of millions of tiny cells called neurons. These neurons are linked together to form long, cable-like structures. Within these nerves, there are different types of neurons, each with its own unique function.
Neurons have three main parts: dendrites, cell bodies, and axons. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons, cell bodies process these signals, and axons transmit the signals to other neurons or target cells. This coordinated effort allows nerve impulses to travel quickly and efficiently throughout the body, ensuring smooth communication and proper functioning of the nervous system.
Introduction to the Mandibular Nerve
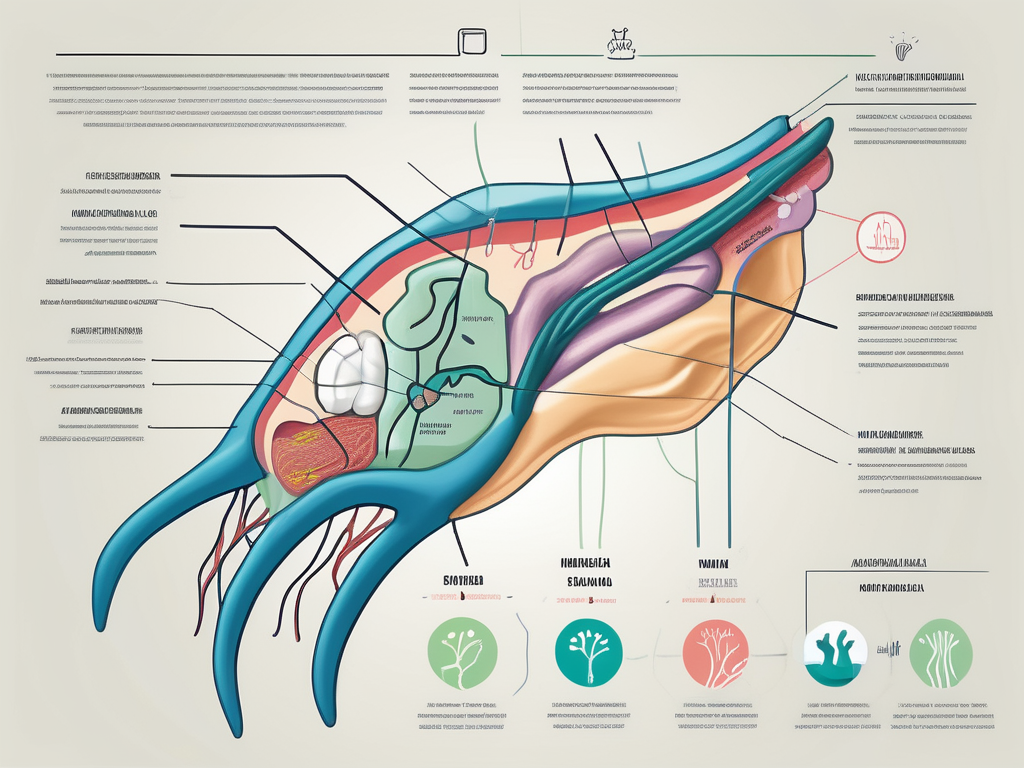
Now that we understand the basics of the nervous system, let’s turn our attention to the star of our article – the mandibular nerve. The mandibular nerve is one of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, which is the largest cranial nerve in our body. It is responsible for providing sensation to our lower jaw, tongue, and certain parts of our face.
The mandibular nerve is a fascinating component of our anatomy, intricately woven into the fabric of our sensory experience. As we delve deeper into its complexities, we uncover the remarkable ways in which this nerve influences our daily lives.
Location and Function of the Mandibular Nerve
The mandibular nerve resides deep within our cheeks, near the lower jaw. It is primarily responsible for transmitting sensations, such as touch, temperature, and pain, from our lower jaw, tongue, and areas around our mouth to the brain. This information helps our brain understand what is happening in our mouth and allows us to respond accordingly.
Furthermore, the mandibular nerve not only conveys sensory information but also plays a crucial role in motor functions. It innervates the muscles involved in chewing, allowing us to enjoy the simple pleasure of savoring a meal or engaging in conversation with ease.
Why is the Mandibular Nerve Important?
The mandibular nerve plays a crucial role in our everyday lives. It allows us to enjoy the taste of our favorite foods, feel the pleasant coolness of an ice cream cone, or even recognize when we accidentally bite our tongue while eating. Without the mandibular nerve, these experiences would be completely different, if not impossible to perceive.
Moreover, the mandibular nerve’s intricate network of sensory and motor functions highlights its significance in maintaining the delicate balance of our oral health and overall well-being. Its intricate connections and vital role in our daily activities underscore the importance of understanding and appreciating the complexity of the mandibular nerve.
Simplifying the Science: Mandibular Nerve for Kids
Let’s make things easier for our young readers! Explaining science can sometimes be a bit complex, so let’s simplify it. Imagine the mandibular nerve as a special connection between your brain and your mouth. It helps your brain receive messages about what’s happening in your mouth and how it feels. It’s like a messenger that brings information to your brain, allowing you to taste, feel, and react to different sensations in and around your mouth.
A Kid-Friendly Explanation of the Mandibular Nerve
Think of your mouth as a play area, and the mandibular nerve as the super-fast wireless connection that keeps your brain updated with what’s happening in the mouth playground. It sends messages about the flavors of your favorite snacks, helps you notice when you accidentally bite your tongue, and even lets you know if something is too hot or too cold to eat. Without the mandibular nerve, our brain wouldn’t know what’s happening in our mouth, and we would miss out on all the fun!
The Mandibular Nerve in Everyday Life
The mandibular nerve is constantly working behind the scenes, even during activities as simple as smiling, talking, or brushing your teeth. It helps you feel the bristles of your toothbrush, warns you if you’re applying too much pressure, and allows you to speak fluently. So, every time you enjoy a tasty treat or show off your beautiful smile, remember to thank your trusty mandibular nerve!
But did you know that the mandibular nerve is not only responsible for helping you taste and feel sensations in your mouth, but it also plays a crucial role in your overall facial expressions? That’s right! This amazing nerve is like a conductor, orchestrating the movements of your jaw muscles, allowing you to chew your food, speak clearly, and even yawn.
Imagine trying to eat your favorite slice of pizza without the mandibular nerve. It would be quite a challenge! Your brain wouldn’t be able to send the signals to your jaw muscles, and you would struggle to take a bite. So, the next time you enjoy a delicious meal, take a moment to appreciate the hard work of your mandibular nerve, making it all possible.
Fun Facts about the Mandibular Nerve
Did you know that the mandibular nerve has some interesting secrets? Let’s uncover a couple of fun facts about this remarkable nerve.
Interesting Aspects of the Mandibular Nerve
The mandibular nerve not only provides sensations to our mouth but also contributes to the movement of our jaw muscles. It enables us to chew our food and speak clearly. So, it plays a dual role in our daily lives, both as a sensory messenger and a motor controller.
Moreover, the mandibular nerve is the largest branch of the trigeminal nerve, which is the fifth cranial nerve. This nerve is crucial for facial sensation and motor functions, making the mandibular nerve a vital component of our overall cranial nerve system.
The Mandibular Nerve and Human Senses
Scientists have shown that certain senses, like taste, are also influenced by the mandibular nerve. This means that when you have a delicious piece of chocolate melting in your mouth, you can thank your mandibular nerve for delivering the delightful experience straight to your taste buds!
Additionally, the mandibular nerve plays a role in controlling the muscles involved in facial expressions. From smiling to frowning, the mandibular nerve ensures that our facial muscles move accordingly, allowing us to convey a wide range of emotions through our expressions. So, next time you flash a smile or furrow your brows, remember to give a nod of appreciation to your hardworking mandibular nerve!
Frequently Asked Questions about the Mandibular Nerve
Let’s address some common questions that kids often ask about the mandibular nerve. Curiosity leads to knowledge, so let’s dig in!
The mandibular nerve, also known as the inferior alveolar nerve, is a crucial branch of the trigeminal nerve responsible for providing sensory innervation to the lower jaw, teeth, and gums. It plays a vital role in our ability to chew, speak, and feel various sensations in our mouth.
Common Questions Kids Ask about the Mandibular Nerve
Q: Can we live without the mandibular nerve? A: While it is technically possible to live without the mandibular nerve, our daily lives and enjoyment of different sensations would be greatly affected.
Q: Is the mandibular nerve the only nerve in our mouth? A: No, the mandibular nerve is one of several nerves in our mouth. Each nerve has its own special role, helping us experience and interact with the world around us.
Answers to Your Mandibular Nerve Queries
Q: Does the mandibular nerve always send the same signals to the brain? A: Not necessarily. Sometimes, our brain can misinterpret the signals sent by the mandibular nerve, leading to sensations like “brain freeze” when we eat something cold too quickly.
Q: Can we train our mandibular nerve to become more sensitive? A: While we can’t directly train our nerves, practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing our teeth regularly and avoiding extreme temperatures, can help keep our mandibular nerve healthy and functioning optimally.
It’s fascinating to note that the mandibular nerve also plays a role in regulating blood flow to the lower part of the face, contributing to maintaining proper temperature balance and overall facial sensation. This nerve’s intricate network of fibers ensures that we can perceive touch, pain, and temperature variations accurately, allowing us to react swiftly to potential dangers or changes in our environment.
Conclusion: The Wonders of the Mandibular Nerve
As we conclude this journey into the world of the mandibular nerve, we hope you have gained a newfound appreciation for this incredible part of your body. The mandibular nerve is more than just a connection between your brain and mouth; it is a gateway to the tastes, sensations, and expressions that make our lives vibrant.
Recap: What We’ve Learned about the Mandibular Nerve
We learned that the mandibular nerve is a critical part of our nervous system, responsible for providing sensations to our lower jaw and mouth. It allows us to enjoy different tastes, feel the texture of food, and pull off that perfect smile. The mandibular nerve is both a messenger and a motor controller, making it an essential player in our everyday experiences.
Encouraging Further Exploration of the Human Body
Remember, this is just the tip of the iceberg! Our body is full of wonders waiting to be discovered. So, keep exploring, stay curious, and never stop learning about the incredible mechanics that make us who we are. The human body is an extraordinary masterpiece, and the mandibular nerve is just one of its many marvels!